Obesity
Symptoms and causes
Symptoms and causesThe difference between being overweight and obesity
The difference between being overweight and obesity- Being overweight is a syndrome in which the quantity of accumulated body fat is so high that it negatively impacts one’s health. The body takes in more nutrients than necessary for the maximum energy needs. This creates a positive energy balance. These excess calories are stored in the form of fat.
- Obesity is a serious form of obesity with serious health risks, such as
- diabetes mellitus type 2 (diabetes)
- arterial hypertension (high blood pressure)
- hypercholesterolemia (too much cholesterol)
- cardiovascular disorders
- joint problems
- depression
- gallstones
- hepatic steatosis (or fatty liver)
- sleep apnoea
- menstrual disorders
These associated conditions - alone or in combination - significantly reduce life expectancy. Obesity is caused by an imbalance between the energy intake and the energy consumption, resulting in fat accumulation and weight gain. Excessive food and alcohol consumption and lack of exercise lead to a positive energy balance. Also genetic factors, metabolic disorders (e.g. hypothyroidism) certain medication and psychological factors can have an influence on overweight.
When do we talk about overweight or obesity?
When do we talk about overweight or obesity?The absolute weight is a bad parameter to decide whether a person is overweight or obese. Since weight should be relative to length, we use the BMI or Body Mass Index , which represents the ratio of length to weight.
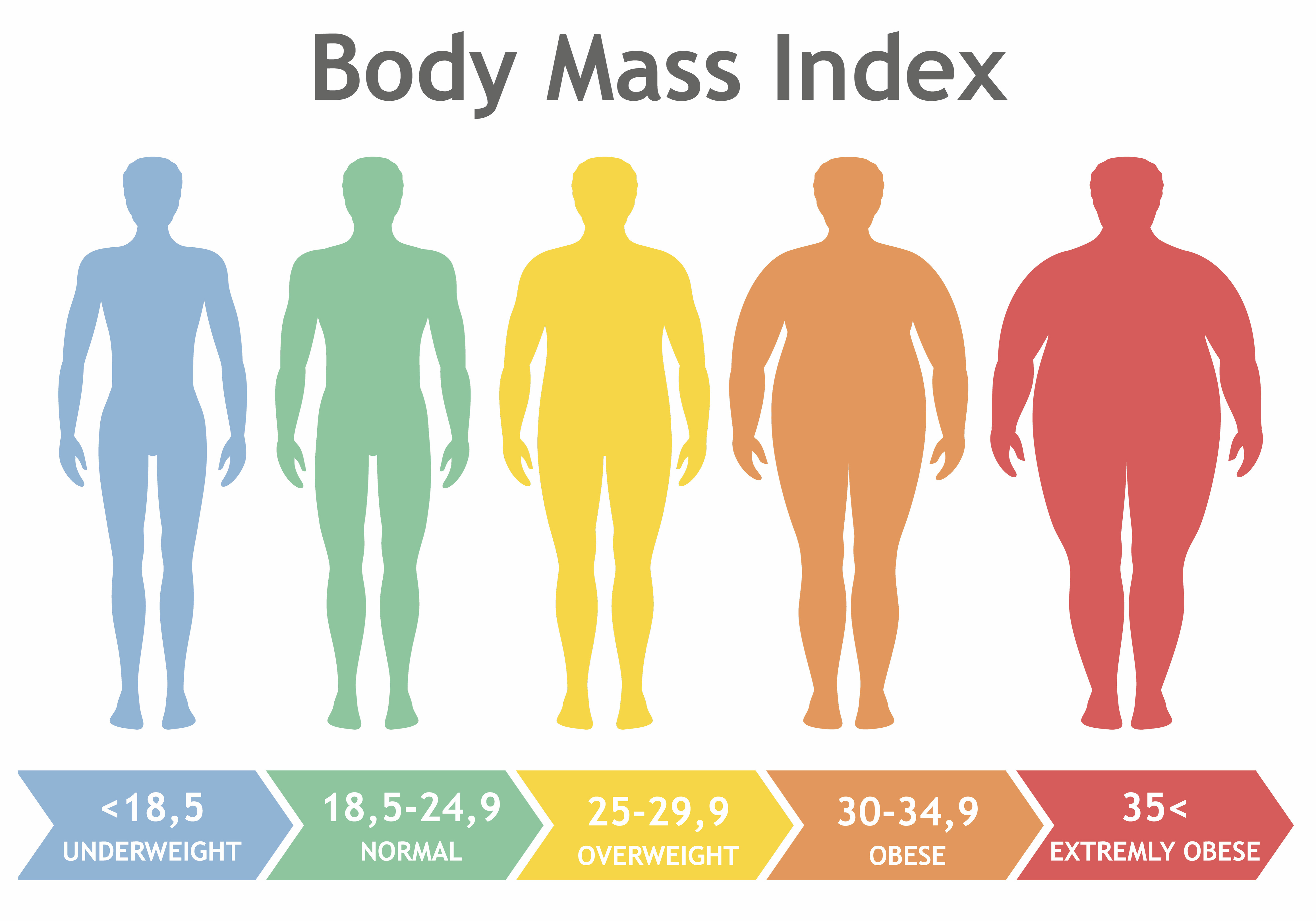
In addition to calculating the BMI, the waist circumference can give an indication of the abdominal fat mass (the amount of fat accumulated at the abdominal level). Fat accumulation around the abdomen is accompanied by serious health risks. There is an increased risk from 88 cm in women and 102 cm in men.
There is an ideal weight for everyone. It depends on several factors (e.g. gender, muscle mass, body structure), which makes the margins of an ideal weight very broad. The values calculated using the BMI method are therefore not applicable to children, the elderly, people with high muscle mass, pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Treatment centres and specialisations
Treatment centres and specialisations
Latest publication date: 15/05/2024
Supervising author: Dr Boer Mirra




