Ergonomic tips - sitting
Sitting in the wrong way for a long time results in a convex lower back, as opposed to the natural, inward curve of the lower back. We therefore need to try and sit for shorter periods and be aware of using a correct seated position that maintains the natural S-curve.
Passive sitting (back supported)
Passive sitting (back supported)- Your feet are resting on the floor
- Support in the lower back
- Evenly spread your weight across both sit bones
- Adjustable
- Pay attention to the natural S-curve
- Maintain an open angle between trunk and hip

Active sitting
Active sitting- Feet resting beneath the chair (to allow for an open angle of the trunk)
- No support in the lower back
- Natural S-curve is maintained
- Evenly spread your weight across both sit bones
- Active sitting requires muscular effort
- Trunk upright

Dynamic sitting
Dynamic sittingThe main message is to limit sitting for prolonged periods of time and to frequently switch to standing or walking. When sitting, the best option is dynamic sitting. This makes us mobilise enough muscle groups to maintain or obtain a good condition of the back and reduces the pressure on the intervertebral discs.

Sitting in the car
Sitting in the car- Ensure an open angle between the upper leg and the trunk (adjust the backrest backward)
- Do not stretch your leg fully when depressing the accelerator
- For long drives: take a short walk every hour
- Your arms are slightly bent when holding the steering wheel
- Get into the car in two steps and bring the seatbelt with you (see picture)
- Bring your leg with you
- Push off when getting out of the car
- Occasionally adopt an active sitting posture, away from the backrest



Sitting at a desk
Sitting at a desk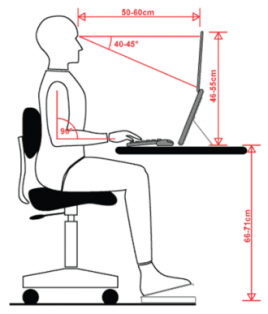
- Place your computer screen and keyboard directly in front of you
- The top of the monitor should be at eye height and your screen at an arm’s length
- Your feet are supported
- Make sure that there is space between the back of your knees and the seat of your chair (width of a fist)
- Open angle between the trunk and upper leg (equal to or more than 90°)
- Armrests and table top are at the same height
- If you use your laptop longer than two hours: use an additional keyboard and a mouse
Latest publication date: 16/05/2024


