Gastric bypass
What is it?
What is it?A gastric bypass is an operation in which the stomach is reduced in size to combat obesity.
The surgeon creates a small gastric pouch of 20 to 30 cc. The small gastric pouch is connected to a one piece of the small intestine (small intestine loop). A part of the small intestine is diverted or 'bypassed'. As a result, food does not come into contact with the digestive juices of the large residual stomach, pancreas and bile before 150 cm. These juices then start digesting the food. The stomach, duodenum and part of the small intestine are excluded from digestion.
The gastric bypass ensures that you will eat smaller amounts and experience a feeling of being full faster. In addition, you absorb fewer calories from your nutrition. The combination of eating less and consuming fewer calories results in weight loss.
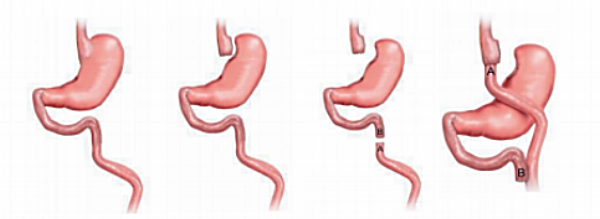
The procedure
The procedureThe procedure takes about 2 hours, although it depends on the type of procedure. A gastric bypass is performed with keyhole surgery (laparoscopy). This requires 5 small holes in the upper abdomen.
We use staples to create a new small stomach reservoir in the upper part of the stomach. The new reservoir no longer has a passage to the rest of the stomach.
Results
ResultsThe gastric bypass is the gold standard and therefore the most common weight loss surgery. The procedure is also fully reversible.
You can usually leave hospital on the second or third day after surgery. In the first three weeks in particular, you will have a modified diet. Afterwards, you are prescribed a vitamin preparation that provides the body with vitamin B12 and iron supplements in particular.
The greatest weight loss occurs in the first year after surgery:
- around 15% of the original weight after 3 months
- 20-25% after 6 months
- 30-30% after 12 months.
A (small) weight gain of 5% after the second post-operative year is quite normal. The main aim of the surgery is not weight loss as such, but to become healthier.
Some advantages:
- Volume eaters and sweet eaters are eligible for this operation, because of a reduced absorption of sugars.
- Reflux symptoms may diminish or disappear.
- Patients do not develop diarrhoea, as most of the small intestine is responsible for digestion.
Side effects
Side effects- During or shortly after surgery: staple-line leaks, bleeding, abscess, thromboembolism...
- Long-term: stomach ulcers, gallstones and internal herniation (entrapment of the small intestine in the abdomen) or obstruction.
- Dumping syndrome is one of the most important side effects after a gastric bypass. It causes nausea, heart palpitations, sweating, dizziness, etcetera shortly after eating sugary or fatty foods or eating too much or too quickly. The symptoms usually disappear by themselves and often improve by lying down. Treatment consists of dietary adjustments in first instance. If this is not effective, medication (antidiabetics or somatostatin) may be started.
- Vitamin and/or mineral deficiencies (iron, vit B12, folic acid) are avoided by taking a daily multivitamin.
- Hair loss and/or brittle nails may occur from the third month after surgery due to significant and rapid weight loss. This recovers of its own accord nine months after the operation.
- Performing a gastroscopy or ERCP with the traditional method (the mouth) is difficult, as the pouch is closed off from the residual stomach.
Cost estimate
Cost estimateCentres and specialist areas
Centres and specialist areasLatest publication date: 06/08/2024



